
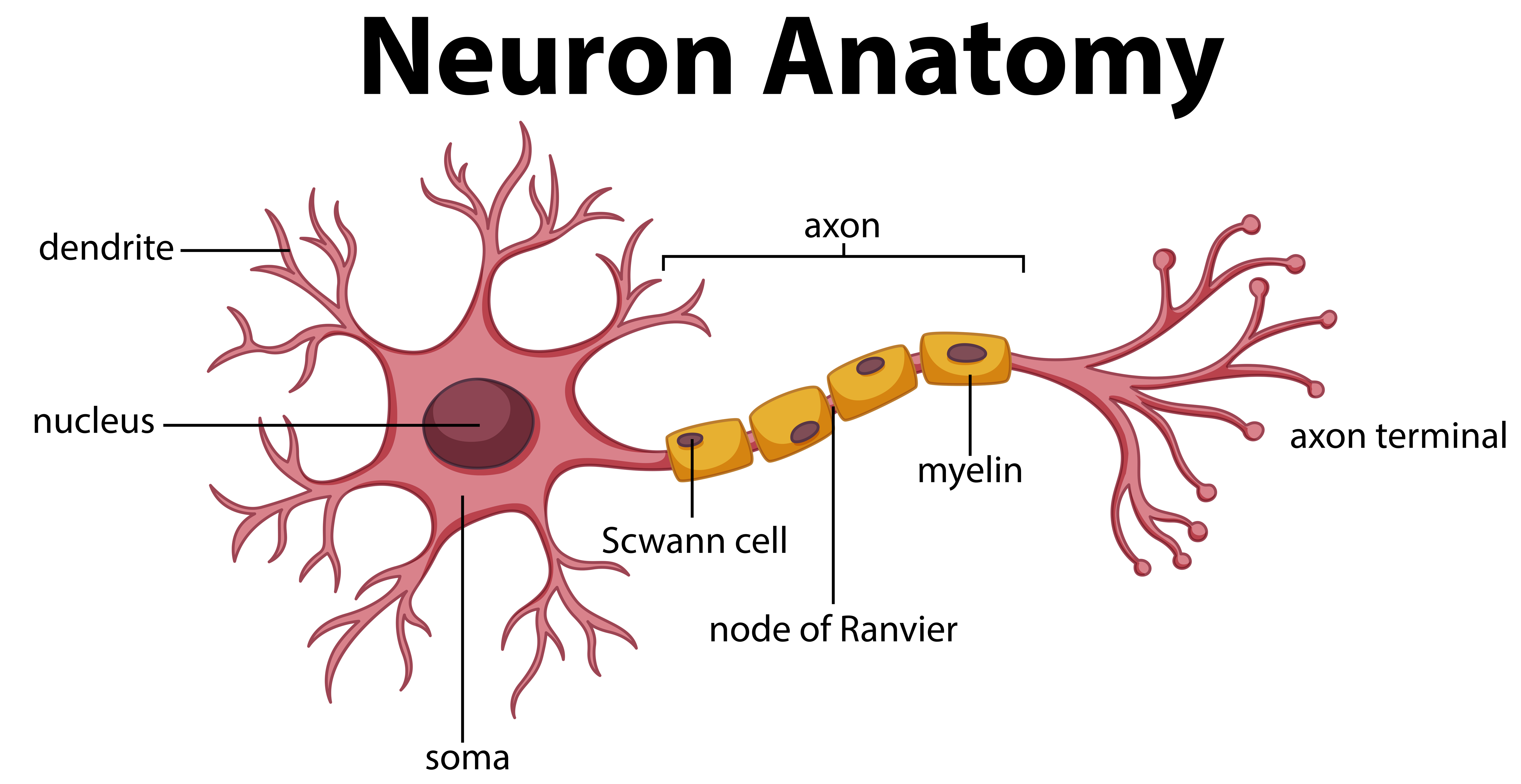
Because of this, a neuron that is no longer able to receive input from lost connections will likely end up dying, unless it is able to establish a new connection with another neuron. This creates damage to the axons so they are no longer able to communicate with neurons and the connection is lost, causing information to "get stuck" as it cannot be effectively passed on. Such a problem commonly occurs in the presence of "axonal shearing" as the structure and connection of the axon with cell body is disrupted or "sheared" from the cell body by trauma forces. In addition, axons are insulated, similar to electrical wires, with a fatty substance called myelin, to keep electrical current strong and flowing directionally.Ībnormal neuronal firing can occur when the signals between neurons are somehow disrupted. Such information is passed from neuron to neuron via the axons, which act like the cable or wires in your house. The dendrites are tree-like structures that receive and gather information from other neurons for delivery to the soma, where the information is processed and as mentioned, the determination is made whether it is important enough to pass along to other neurons. The soma can be thought of as the "brain" of the brain cell, as it processes the input/information into the cell and determines if it is important enough to pass along to another cell. To better understand this process, it is important to understand the parts of a neuron, including the soma, dendrites and axons. If the neurons are continually exposed to a stimulus of fixed duration, it seems they get tired.The process of normal neuronal firing takes place as a communication between neurons through electrical impulses and neurotransmitters. These neurons, located in the brain’s supramarginal gyrus (SMG), fire in response to a specific length of time. Scientists have discovered that time-sensitive neurons in the brain could wear out and distort our perception of time, publishing their findings in the Journal of Neuroscience in 2020.
If time seems to go more slowly when you’re boiling the kettle or waiting for a bus, it might not just be your imagination. You can watch the 2018 SCINEMA International Science Film Festival Best Short Film winner, KCLOC, here. Well, according to research published in 2020, time really does fly when we’re having fun and it’s due to a specific set of time-sensitive neurons that skew our perception of the passage of time. One question posited by the film is: why does time speed up when you’re having the time of your life, but slow down when you’re hating it?

KCLOC is a 3D animated short film that explores peoples’ perception of time.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
